Sunday, December 13, 2009
Video Links
- Cloning video
video.google.ca/videoplay?docid=246187639814358296&ei=NH4lS6qJIIHKqgPvps3JAQ
q=cloning&hl=en&view=3# - Dolly, the sheep video
References
http://www.clonesafety.org/cloning/facts/process/
http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/whatiscloning/
http://science.howstuffworks.com/genetic-science/human-cloning2.htm
http://www.religioustolerance.org/cloning.htm
http://socialissues.wiseto.com/Articles/FO3020640070/?print
http://atheism.about.com/library/chronologies/blchron_sci_cloning.htm
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/ethical-issues-of-cloning.html
http://www.publicagenda.org/files/charts/rf_medresearch_cloning_human_treatments2.png
http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/tech/cloning/cloningmyths/images/instantclones.gif
http://researchers.in.th/file/sudjai/cloning.jpg
www.gdargaud.net/
http://www.publicagenda.org/files/chart/pcc_medresearch_oppose_cloning_religious_beliefs.png
Ethical Issues
History
1888 - Wilhelm Roux, for the first time, experimented with the germ theory resulting in supporting Weismann’s theory. He destroyed one of the two cell frog embryo with a hot needle, and got a half-embryo.
1902 - Hans Spemann successfully split a two celled salamander embryo and the cells grew. He disapproved Weismann’s theory that with every division information was lost.
1944 - Oswald Avery found that DNA carries a cell's genetic information.
1952 - Robert Briggs and Thomas J. King did the first cloning of an animal. They cloned northern leopard frogs.
1953 - Francis Crick and James Watson, discovered the structure of DNA while working at Cambridge's Cavendish Laboratory.
1962 - Biologist John Gurdon announced that he had cloned South African frogs using the nucleus of fully differentiated adult intestinal cells. This demonstrated that the information doesn’t diminish as it becomes specified.
1967 - The enzyme responsible for binding together strands of DNA was isolated.
1969 - James Shapiero and Johnathan Beckwith declared that they had secluded the first gene.
1972 - Paul Berg combined the DNA of two different organisms, creating the first recombinant DNA molecules.
1973 - Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer created the first recombinant DNA organism using recombinant DNA techniques pioneered by Paul Berg. Taking DNA from two different organisms and combining them.
1977 - Karl Illmensee and Peter Hoppe created mice with only a single parent.
1978 - Baby Louise, the first child conceived through in vitro(made in a laboratory vessel or other controlled experimental environment rather than within a living organism or natural setting) fertilization, was born.
1979 - Karl Illmensee declared that he cloned three mice.
1983 - The first human mother-to-mother embryo transfer was completed.
1984 - Steen Willadsen cloned a sheep from embryo cells. By sing the process of nuclear transfer to clone the first mammal.
1985 - Ralph Brinster created the first transgenic livestock: pigs that produced human growth hormone.
1986 - Neal First, Randal Prather and Willard Eyestone used early embryo cells to clone a cow.
1993 - Human embryos were first cloned.
July 1995 - Ian Wilmut and Keith Campbell cloned two sheep, Megan and Morag by using differentiated embryo cells.
July 5 -1996 Dolly, the first organism ever to be cloned from adult cells was declared.
February 23, 1997 - Scientists at the Roslin Institute in Scotland officially announced the birth of "Dolly".
July 1997 - The scientists Ian Wilmut and Keith Campbell, who created Dolly, also created Polly, a Poll Dorset lamb. It was created from skin cells grown in a lab and they were genetically modified to contain human gene.
1997 - Same scientists that created Dolly, cloned mouse. Shortly afterward, 22 of her cloned siblings joined them (some of whom were cloned from clones).
2003 - A tropical fish that is fluorescent bright red becomes the first genetically modified pet to go on sale in the US.

Wednesday, December 9, 2009
Applications/Uses
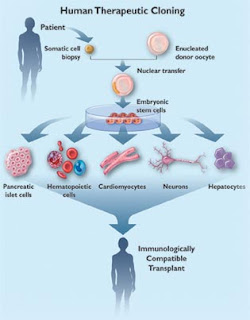 Therapeutic cloning is used when DNA is taken from a sick organism, and then inserted into a donors egg. After this process the egg acts like any fertilized egg. Stem cells are removed from the embryo, and then any kind of organ or tissue can grow from these stem cells to treat diseases.
Therapeutic cloning is used when DNA is taken from a sick organism, and then inserted into a donors egg. After this process the egg acts like any fertilized egg. Stem cells are removed from the embryo, and then any kind of organ or tissue can grow from these stem cells to treat diseases.DNA cloning is used to clone an existing animal. For this cloning tecnique to work the DNA from an ovum (female reproductive cell) is removed and replaced with the DNA from a cell removed from an adult animal. It it is then fertilized and called a pre-embryo, and develop into an exact clone.
Brief Description
 Cloning is the recreation of an organism that is exactly the same. In order for anything to be a clone, every bit of DNA has to be the same. Dolly the sheep is famous for being cloned. This means that there is a sheep that is just like her, it has every single bit of DNA that she has.
Cloning is the recreation of an organism that is exactly the same. In order for anything to be a clone, every bit of DNA has to be the same. Dolly the sheep is famous for being cloned. This means that there is a sheep that is just like her, it has every single bit of DNA that she has. Other types of cloning are DNA cloning, and therapeutic cloning.




